What are Microplastics? Why are They Bad For You?
What are Microplastics? Why are They Bad For You?
Article provided by Keaton Smith from Bivo
I had known that plastic wasn’t great for you for a while. I tried not to microwave my food in plastic, opted for my wooden reusable utensil set over a disposable fork, and avoided disposable plastic bottles.
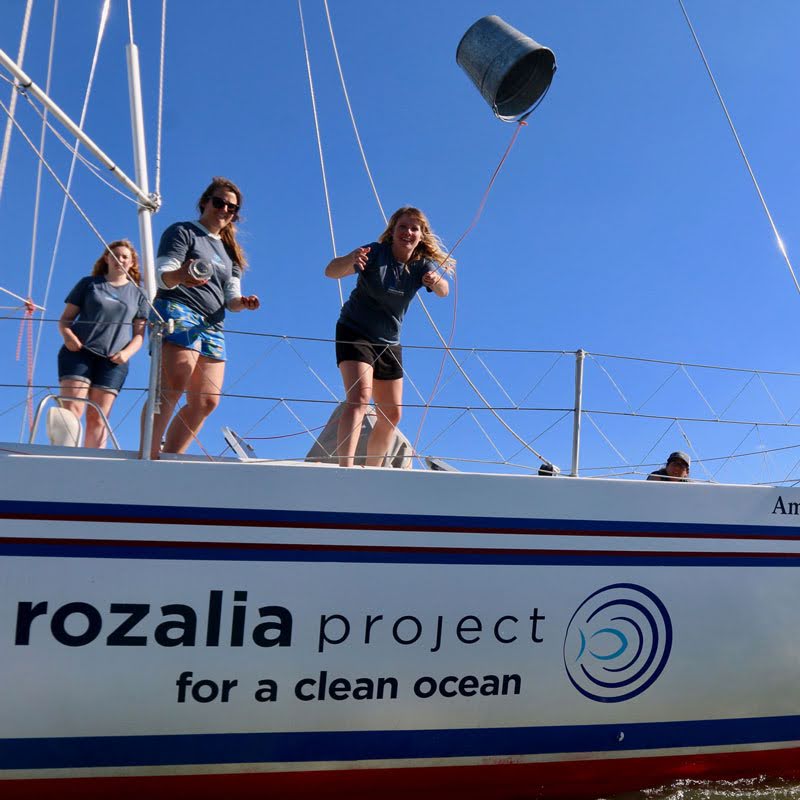

The team from Rozalia Project for a Clean Ocean conducting microplastic research in the Hudson River to both understand and prevent the problem.
But I was fuzzy on the details. Wait, what is plastic supposed to do to me again? What exactly is bad about it? How big of a deal is this issue?
A few months ago, we started seeing more and more news articles about micro and nanoplastics, prompted by the release of a big study from Columbia University. This study found some scary stats about the sheer number of nanoplastics in plastic water bottles.
To make sure I was fully up to speed on the science of plastic, I sought out an expert to answer some of the most common questions we see about micro and nanoplastics.
For today’s post, I interviewed Rachael Z. Miller. Rachael is a National Geographic Explorer and the founder of the Rozalia Project, a non-profit that tackles the problem of marine debris–which includes waste like old fishing gear, consumer debris and microplastic and microfiber pollution. They conduct research from a 60ft sailing research vessel and use underwater robots to pick up samples from the ocean floor.
What are microplastics? What’s the difference between microplastics and nanoplastics?
Microplastics are plastic particles that measure between 5mm (half the size of your pinkie nail) and 1 micron. They include pieces intentionally manufactured at a small scale (like face glitter) as well as pieces that are fragments of larger plastic items.
Synthetic microfibers are included in the umbrella of microplastics. Microfibers, in general, are tiny fibers that have broken off of longer fibers. While these microfibers can be non-synthetic (natural), many are synthetic (made from plastic) and most are treated with chemicals (think: fabric softener and dye-setting agents) that would be harmful to humans and the environment.
Nanoplastics are even smaller. One micron and smaller. (For reference, 70 microns is about the width of a strand of hair, so nanoplastics are way smaller than that).
Scientists are only just starting to publish studies on nanoplastics so the research is limited- mostly because the technology available to study something this small is so new that it isn’t widely used yet.
How prevalent are micro and nanoplastics in the environment?
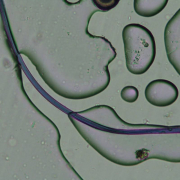
A blue polyester fiber found in the Hudson River.
Unfortunately, they are everywhere. In the ocean, on the hiking trails, in the dust in your house. They’re even in remote parts of the world. Rachael and her team found microplastics, mostly microfibers, in the Southern Ocean, the Falkland Islands, and the Antarctic Peninsula.
Why is this bad?
Plastics are known endocrine disruptors, meaning they wreck or mess with reproductive systems. Additives associated with plastic manufacturing can also cause harm to living creatures. While the majority of studies from the last 15 years have been focused on establishing myriad harms that microplastics can cause to creatures in and around the water, it has only been over the last few years that studies to understand the implications for humans have surfaced.
Recent studies published in March 2024 (here and here) have established correlations (not causations, but still enough to give us a scare) between the presence of microplastic in various parts of the human body, including everything from behavior change to disrupted gut biome, reduced fertility and even heart attack, stroke and death.
While to date, there’s no ‘patient zero’ that establishes a causal link between microplastics and a particular issue, for Rachael, at least, the evidence to reduce exposure to plastic is extremely compelling.
How to reduce your own exposure to microplastics
Finally, there are many steps we can take in our own lives to reduce our own exposure to microplastics. While the issue may be more on a systemic level, here are some tips to think about moving forward:
- Use less plastic in your daily life
- Avoid drinking and eating directly from plastic
- Avoid buying food wrapped in plastic
- Educate yourself and help out your community (Rozalia Project has some great programs, for example)
How to reduce microparticle shedding
To help slow the spread of microplastics, there are lots of small things we can do.
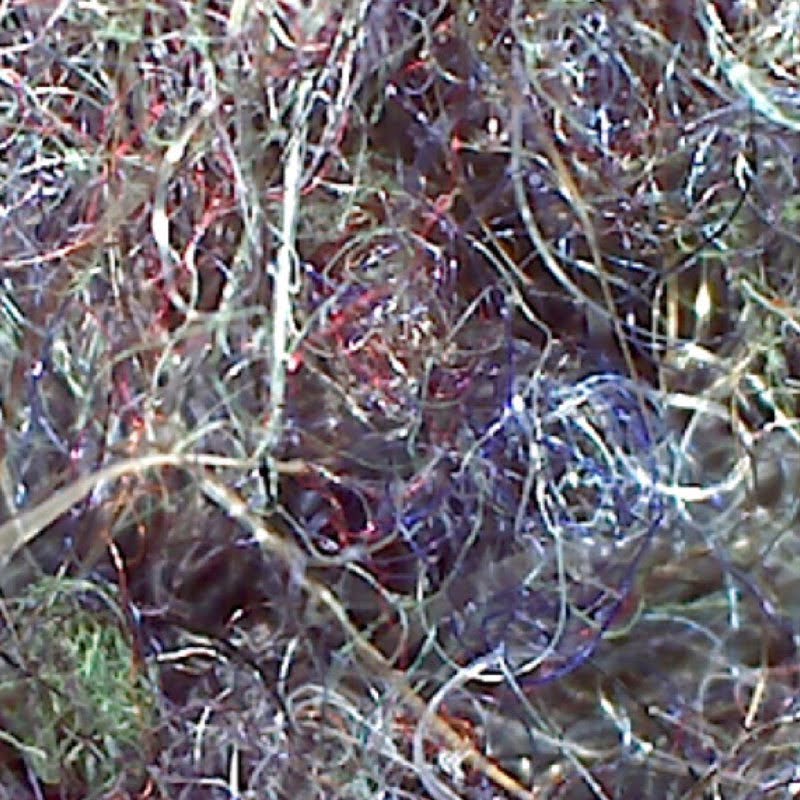

A bundle of microfiber filtered from a load of winter laundry done in a top-loading washing machine.
One way that microplastics and microfibers enter the waterway is via washing machines. Microfibers shed off of the clothing being washed and exit the machine along with the water, entering the local waterway and making its way to the ocean. Rachael shared some tips on reducing this shedding:
- Wash clothes in cold water
- Only wash clothes that are dirty
- Always do loads that are 3/4 full
- Use this laundry ball to trap microfibers
While most wastewater treatment plants are able to stop the vast majority of the fibers that arrive in the influent, it is likely that fibers like these can still end up on our public waterways as part of fertilizer.
A better solution is to prevent this from happening in the first place with more resilient clothing, better washing settings and techniques and through the use of in-drum, in-line or external filtering devices.
Another way that microfibers shed is just when we wear our clothing. Rachael suggests strategizing around what we’re wearing:
- Try wearing high-shedding clothes (think: wooly/ fleece layers) as base layers and low-shedding clothes (like a hard shell) as top layers.
- Buy high-quality clothing and take good care of it
- Ask your favorite outdoor clothing brands to improve the quality of what they offer. Tell them you want and will buy from them: low-shed technical gear made out of something that’s bio-derived (made from natural materials) and bio-benign (won’t harm the environment).
Have additional questions about microplastics? Reach out to us and we will do our best to help: thirsty@drinkbivo.com.
About Bivo
Keaton Smith is Bivo’s marketing specialist. Bivo is the first stainless steel water bottle engineered for cyclists. Bivo’s founders Robby and Carina were tired of drinking out of plastic cycling bottles and wanted to create a healthier, more enjoyable alternative. Bivo bottles are easy to clean and keep your water tasting pure.